Maintaining a healthy diet and integrating exercise into your daily lifestyle may not remove unwanted fat. These excess fat deposits are usually stubborn to burn off and may be present due to some health conditions, pregnancies, age, or genetics. However, they can be removed through a process known as “Liposuction,” resulting in an improved body shape and proportion.
What is liposuction?
Liposuction, also referred to as liposculpture suction, lipoplasty, suction-assisted lipectomy, or simply lipo, is a plastic surgery procedure. The aim is to improve body contours and proportion by removing excess fat deposits to refine and reshape specific body areas.
Target areas for fat removal include the
- Hips
- Abdomen
- Buttocks
- Thighs
- Neck
- Arms
- Cheeks
- Breasts
- Knees
- Chin
- Ankle
- Back
Although you may lose some weight during the procedure, liposuction may not be considered a weight loss surgery. Specifically, the amount of fat removed during a liposuction section ranges from 3 to 4 liters. Further attempts to reduce more significant amounts of fats may increase risk factors and complications during and after the surgery.
Also Read – Body-Jet Liposuction: Procedure, Benefits, Risks, And Costs
A certified plastic surgeon, cosmetic surgeon, or dermatologist performs the Liposuction procedure. It involves using a narrow, hollow tube – cannula and a suction device – an aspirator to suction fat deposits under the skin. The technique contours targeted areas of the body and is performed under local, regional, or general anesthesia.
Liposuction may be performed alone or alongside other plastic surgery procedures, such as tummy tuck, facelift, and breast reduction (2).
Who is the ideal patient for liposuction?
Liposuction is most beneficial and ideal for you if
- You are at or near your ideal body weight
- Have good skin elasticity and muscle tone (3)
- Have struggled with losing fat deposits in specific body areas despite diet plans and exercise
- Healthy, without health conditions that could lead to surgery complications. Such as coronary artery diseases, diabetes, weak immune systems, and restricted blood flow (4).
Why carry out liposuction?
The liposuction procedure is carried out for two purposes,
- Cosmetic purposes – which is to change body shape, solely for aesthetics.
- Reconstructive purposes – to treat certain health conditions, usually removing lipomas – fatty lumps between the skin and muscle layers. This procedure is used in medical conditions such as Lymphedema and Lipoedema. Lymphedema is the swelling of the arms and legs resulting from excessive fluid collection within the tissues over a long-term period (5). Lipoedema is a condition of abnormal fat deposits under the skin in the buttocks, thighs, and legs (6).
Different types of liposuction
Liposuction comes in various types, distinguished by the techniques employed. These methods can be categorized based on the cannula’s mechanism of action and the quantity of injected fluid. Surgeons may occasionally utilize two or more techniques in a single session.
Micro-cannula technique
This technique is specific for the diameter of the cannula used – a stainless steel tube with an outside diameter ranging from 1mm to 3mm. It is inserted through an incision or small opening into the subcutaneous fat.
Suction-assisted Liposuction (SAL)
This technique is also referred to as “suction-assisted lipectomy.”
Tumescent Liposuction
This technique is the most common type of liposuction. The word “tumescent” means swollen and firm and involves anesthesia in the surgery process (7).
A large amount of sterile solution – usually up to three times the amount of fat intended for removal is injected into the targeted areas of excessive fat deposits. The sterile solution is a lidocaine, epinephrine, and IV salt solution. Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that helps to relieve pain during and after surgery. Epinephrine is a drug that contracts blood capillaries and helps to reduce blood loss, bruising, and swelling. The IV – intravenous salt solution helps remove the fat easily. The targeted tissue becomes swollen and firm when injected with the fluid mixture. The surgeon then makes incisions into the skin and inserts the cannula connected to a vacuum that suctions the fats and fluids from the body.
Water-Jet Assisted Liposuction
This technique is used for lipedema patients who require lymph-sparing liposuction. It involves removing fat using a fan-shaped jet of water containing the anesthetic solution.
Lymph-Sparing Liposuction
This technique is used in the removal of lipedema fat. It is not performed alone, alongside tumescent liposuction or Water-jet assisted suction technique.
Also Read – Liposuction Recovery: Speed It Up With This Comprehensive Guide
Power-assisted liposuction
Otherwise known as the vibrating cannula, this technique involves the rapid movement of the cannula in a back-and-forth motion. It allows the surgeon to pull tough fat rapidly and with more precision. Usually, this technique is used to remove large volumes of fat, scarred areas or in a scenario where liposuction has been carried out previously (8).
Fibro-Lympho-Lipo-Aspiration Liposuction
This technique is used for the reconstructive liposuction processes. Extra care is given to the lymphatic vessels, which are already abnormal in this scenario. Hence, only small, blunt cannulas are used; specifically, only the longitudinal orientation of cannulas is used at critical junctures. This surgery is more time-consuming and intended to relieve symptoms such as ameliorate disability pains, halt disease progression, and improve life quality.
Ultrasound-assisted liposuction
As the name implies, this technique uses ultrasound vibrations to rupture the fat cell walls into a liquid form for easier removal. It can be done in two ways: internally below the skin surface with a small, heated cannula or externally above the skin surface with an emitter. In addition, it may help remove fat from dense, fiber-filled areas of the body (9).
Laser-assisted Liposuction
Also known as lipolysis, it uses laser energy to liquefy/emulsify fat deposits. A small cannula is used; hence, this technique is adopted in small, confined areas such as the face and chin. An advantage of this procedure is that energy from the laser stimulates collagen production, preventing skin sagging after surgery. Collagen is a fiber-like protein that helps maintain skin structure.
Super-wet technique
In the tumescent technique, the fluid injected is up to three times the fat to be removed. However, in this technique, the fluid injected equals the amount of fat to be removed. This liposuction procedure takes less time but requires sedatives – medicine that makes you tired.
What to expect – The Process
Your surgeon will select the appropriate liposuction technique to achieve your desired goal. Sometimes, a variety of methods is combined for a procedure.
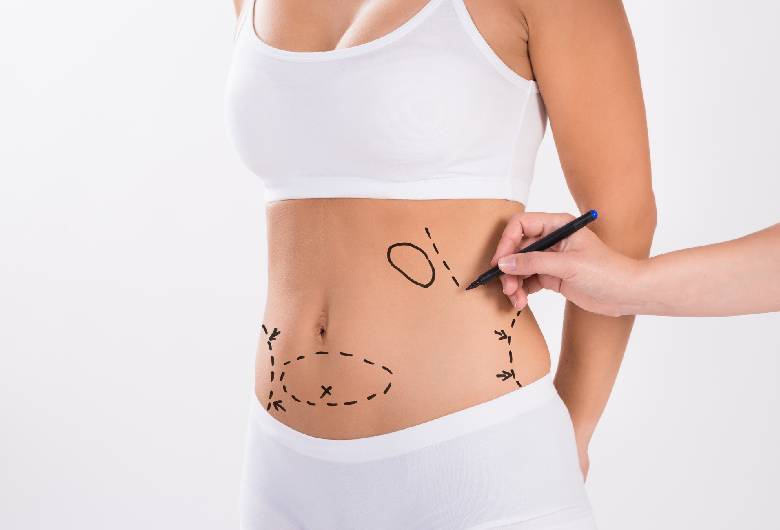
- The surgical team will prepare you, mark targeted areas on your body, and take photos – so that before and after photos can be compared.
- The liposuction machinery to be used for the surgery will be set up.
- IV fluid lines will be situated to help regulate fluid levels during the surgery.
- You will receive anesthesia – which induces a temporary state of unconsciousness, for your comfort during the procedure.
- During the surgery, small incisions or skin punctures will be made on your skin in well-hidden natural body creases.
- The surgical team will monitor your blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen level throughout the procedure.
- The procedure may last for hours, depending on the extent of fat removal.
- At the end of the procedure, incisions are closed up with sutures; sometimes, small tubes are placed at incision sites to drain body fluids.
- You may lose a lot of fluid and may need fluid replacement – this will be done intravenously.
- After the surgery, you will wake up in a recovery room, covered with a compression garment fitted for the targeted areas.
- Expect some numbness, pain, swelling, and bruising from the procedure. This typically subsides within a few weeks (10).
- You may return to non-strenuous work after 2 to 3 days, but this will vary depending on the techniques used and your health conditions.
- The treated area may take up to 6 months to settle and take up a leaner appearance.
Also Read – Is Mommy Makeover Safe? 5 Essential Things Explained By A Certified Plastic Surgeon
How you prepare for surgery
- Discuss expectations during and after the surgery extensively with your surgeon – including risks and possible complications.
- Be honest about every underlying health condition, medical history, medication, and supplement – including your entire health history and detailed weight history.
- You may be required to run lab tests before the procedure.
- You may be required to stop taking certain medications at least three weeks before surgery.
- You may be required to stop smoking at least two weeks before the surgery – smoking hinders wound healing.
- You may be required to avoid shaving and all hair removal before surgery to prevent ingrown hairs.
- As a woman, you may be required to stop taking contraceptive pills.
- You may be required to stop all forms of consumption after midnight the night before surgery.
- You may be required to sign a consent form confirming your knowledge of the benefits and risks of the procedure (11).
- Have someone drive you to the hospital on the day of surgery and make arrangements for a possible overnight stay.
- Arrange someone to drive you home afterward and possibly stay with you for at least 24 hours.
Side effects and risks
Like every surgical procedure, liposuction has its underlying risks and possible complications. In addition, the following are possible unpleasant side effects.
- Severe bruising – This may last for weeks.
- Paresthesias – The nerve compression at the liposuction site, resulting in intense sensitivity, could be pain or numbness and may be chronic or temporary.
- Inflammation – Fluids may keep oozing from the incision, and swelling may stay up to 6 months.
- Thrombophlebitis – A blood clot in the vein. This is life-threatening and represents more than 23% of liposuction surgery deaths.
- Withered, wavy, or bumpy skin – This appearance of contour irregularities is usually a result of poor skin elasticity.
Infection - Internal organ puncture – visceral perforations, an infrequent occurrence
- Death – Occurs in about one per ten thousand cases and may be associated with anesthesia.
- Kidney, lungs, or heart problems – Changes in body fluid levels during injection and suction may cause these problems.
- Pulmonary embolism – a life-threatening complication involving blockage of blood circulation in the lungs resulting from fat getting into the blood vessels.
- Pulmonary edema – an accumulation of injected fluids in the lungs.
- Allergic reaction – allergy to materials or medications used in the surgery.
- Skin burns resulting from friction movement of the cannula.
- Seroma – The accumulation of serum in areas where fat tissues have been removed (12). The serum is the straw-colored liquid from blood.
- Skin necrosis – Tissue death, the skin above the liposuction site changes color and falls off; this area may also become infected with bacteria.
- Skin deformities at the site of the liposuction after the procedure.
- Lidocaine toxicity: in rare circumstances, this anesthetic administered with fluids during liposuction may have a toxicity occurrence, causing severe heart and central nervous system problems.
If you experience shortness of breath, chest pain, excessive bleeding, or an unusual heartbeat after the surgery, call your surgeon immediately.
Summary
Liposuction is a plastic surgery procedure. It aims to improve body contours and proportion by removing excess fat deposits to refine and reshape specific body areas. Although you may lose some weight during the process, liposuction may not be considered a treatment for obesity, removal of stretch marks or cellulite. The liposuction procedure is carried out for either cosmetic or reconstructive purposes. And is ideal for patients who have struggled with losing fat deposits at specific body areas, despite diet plans and exercise. There are various liposuction techniques, categorized by the mechanism of action of the cannula, as well as the amount of fluid injected. As with surgical sessions, there are risks and possible complications, discuss extensively with your surgeon on expectations during and after the surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Can liposuction remove fat permanently?
Yes, the fat cells removed during liposuction are gone permanently. Maintaining a “post-lipo weight” will ensure the non-accumulation of fat shortly.
How long before the results of your liposuction become visible?
After the surgery, the treated areas will get a leaner appearance. Visible changes can take as long as six months to become visible.
Can you lose weight via liposuction?
Although you may lose some weight during the session, liposuction is not classified as a weight-loss technique.
References –
- “Strategies for Reducing Fatal Complications in Liposuction” – ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- “Liposuction” – plasticsurgery.org
- “Surgery: Basic Science and Clinical Evidence” – books.google.com
- “Liposuction” -mayoclinic.org
- “What is lymphedema?” – medicalnewstoday.com
- “Liposuction” – NHS. uk
- “Does tumescent liposuction damage the lymph vessels in lipoedema patients?” – journals.sagepub.com
- “Advances in Liposuction” -journals.lww.com
- “Innovation in Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery Lipoplasty” -springer.com
- “Tumescent Liposuction” – ucsfhealth.org
- “What is liposuction?” – medicalnewstoday.com
- “Updates and Advances in Liposuction” -academic.oup.com